1. Introduction
In this era of globalization, almost everyone is affected by the impact generated by technological developments. Everyone has access to the conveniences provided, such as easy access to information, wider engagement between people, communication that can be done instantly, and others. Globalization has changed the way people live their lives, from their routines to the attitudes and characters that make them truly human. These involvements are not easy to let go of, as people‘s lives have become embedded with the conveniences that these technological developments have provided. Globalization has made life easier for society as a whole.
Many sectors of the economy are affected as a result of technological development. The ease with which a natural resource can be obtained, the efficiency and effectiveness of a company increase with the ease of mass production and cost efficiency being implemented, and newer knowledge changing outdated ways and methods are some examples of the overall influence of globalization on human life. Although globalization has almost as many negative effects as positive ones, humans will continue to evolve, with technology becoming better than it is today.
Another impact generated by globalization is the emergence of new forms of access in everyday life through technology. One example of this impact is the emergence of digital business. With the convenience provided through the Internet, digital business changes the way people conduct transactions, namely, buying and selling goods or services through the Internet. Buyers can more easily access and order more of the products they are looking for at the quality, price, and brand they want, while sellers can more easily sell their goods to a wider range of buyers, thus increasing their overall sales. The execution of transactions can be done digitally as well, where they can use digital money (E-Money) to speed up transactions. The emergence of digital businesses led to the rise of digital entrepreneurs.
Young entrepreneurs should take advantage of this opportunity in this digital era by using the technology that has been provided and has been made easy to access and use so that they can become business owners who are superior to other existing businesses. Such entrepreneurs should remain innovative, be diligent in learning things related to their business, exploit available opportunities, have a great passion for running their business, and be ethical and socially responsible entrepreneurs. Thus, it is certain that the entrepreneur will be successful, in both traditional business platforms and digital businesses. This paper will discuss four main points, which are as follows: (1) describing the definition of digital entrepreneurship, (2) elements and models of digital businesses for digital entrepreneurs, (3) the opportunity of digital business for digital entrepreneurship, (4) differences between digital business and traditional business, and (5) how to become a digital entrepreneur.
2. Research methodology
This research uses descriptive qualitative research and literature review method. Descriptive research has been described as a research for the purpose of explaining characteristics and situations that are observed (1). Qualitative research means that collects narrative data in words to answer the research questions posed (2). Literature review is a method of research that collects books, web pages, articles, and supporting documents to assist in answering research questions.
3. Research discussion
3.1. Describing digital entrepreneurship
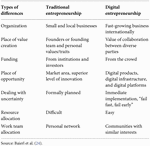
Traditionally, some of the uniqueness of an entrepreneurship from other types of business is the number of people who carry it out, the way they deal with risks and opportunities, the utilization of opportunities, the use of available resources, and a focus on making a better product or service. Entrepreneurship is a type of business that involves a person or several people who have innovation, do it with strong motivation and purpose, and seek and use these opportunities to the maximum so that what they do will succeed. Entrepreneurs play with the uncertainties that exist in their environment, both in the internal environment of their business and in the external environment of the business such as the economic situation. Due to digitalization, traditional entrepreneurship will change and be replaced by digital entrepreneurship, otherwise known as digital entrepreneurship.
Digital entrepreneurship as a term combines the word “Digital” and “Entrepreneurship.” Digital has been defined by Merriam-Webster as using or characterized by computer technology (3), while Entrepreneurship is defined as a business or social person who disrupts the economic order by seizing opportunities, such as introducing new products and services and new methods of production, converting opportunities into marketable ideas that adds value through time, money, effort, and skills, and controlling resources to create innovate economic organization for gaining revenue and growth under certain conditions, risks, and uncertainty (4–6). Combining these two definitions, it can be defined as a person who builds their business with the help of existing technology to find and use potential opportunities, creating new products and services whether it is physical or digital, and to better understand the current condition, risks, and uncertainties that could affect the business. Other authors also defined digital entrepreneurship as follows:
1. It involves the application of traditional entrepreneurial tenets and principles, which have long been utilized in the service of social uplift and advancement, to the cause of intellectual property empowerment in the digital context (7).
2. It is the pursuit of opportunities based on the use of digital media and other information and communication technologies (8).
3. It involves the practice of seizing digitally enabled innovation opportunities discovered in their everyday life to build new business ventures (9).
4. (In EC Digital Entrepreneurship Monitor) It is the act of entrepreneurship that accepts all new ventures and the transformation of existing businesses that drive economic and/or social value by creating and using novel digital technologies (10).
5. It is the phenomenon associated with digital entrepreneurial activity, which consisted of pursuiting value generation, through the creation or expansion of economic activity, by identifying and exploiting new Information Communications Technology (ICT) or ICT-related products, processes, and markets (11).
6. (In European Commission) It involves the use of digital technology by digital entrepreneurs who hold and transform the existing business into the new venture in IT, which drives economic and social value toward digital technology (12).
In short, digital entrepreneurship is an entrepreneurship that has been digitized, namely, the values, methods, and implementation of traditional entrepreneurship that has involved digital changes. Digital entrepreneurship changes the way entrepreneurs deal with risks, seek and use opportunities, how to use limited resources, and create a product or service supported by adequate technology and supports the way entrepreneurs get financial assistance to build their business and facilitate interaction with consumers through feedback. Hence, in digital entrepreneurship, there are differences that involve several new things compared to traditional entrepreneurship, namely:
1. New ways to find new customers for entrepreneurial ventures.
2. New ways to plan and offer products and/or services.
3. New ways to generate revenue and reduce costs.
4. New opportunities to cooperate with other platforms and other partners.
5. New sources of competitive opportunities, risks, and benefits.
Wallin et al. (in Giones & Brem) stated that digital entrepreneurs use technology as an input factor to become a dominant player in their sector and rival their competitors (13). Digital entrepreneurs use the online dimension to find new customers, create new business ideas, and improve their business based on available data. This creates a new experience for both entrepreneurs and consumers who use digital technology to interact with these entrepreneurs, where the scope of interaction is wider and it is easier to provide the feedback that entrepreneurs need to grow.
3.2. Elements and models of digital business for digital entrepreneurs
It is important to understand that although digital business has been a concept that existed since the dawn of the Internet and its existence has been older than digital entrepreneurship, the introduction of digital entrepreneurship contributes to revolutionizing businesses way more than before. The concept of digitalization in entrepreneurship has affected businesses, digital or physical, in a way that they can conduct research and find new ideas to create profit for them.
Renda et al. in Bisht et al. stated that there are four main elements in digital entrepreneurship, which are robust and continually surfacing computing clout, modularity, the end-to-end design of the Internet and its unbiased nature, and the digital nature of information goods (14). These elements assisted digital entrepreneurs to create a digital business, which allows products to reach out to the world quickly at a low cost and with the attributes of the Internet (14). Digital business (sometimes called E-Business) has been defined by Wirtz (15) as the initiation as well as the partial or full support, transaction, and maintenance of service exchange processes between economic partners through ICT. Jackson, Harris, and Eckersley explained the following three main features of digital businesses (16):
1. Make use of electronic devices for processing and communicating data.
2. Allow increased integration of databases and hardware devices.
3. Enable users to engage interactively with systems and services provided.
However, according to Hinchliffe in Afshar, the key elements of digital business are more straightforward, as shown in Figure 1 (17).

Figure 1. Elements of digital business. Source: Afshar (17).
According to Figure 1, a digital business must have these four main key components, such as understanding a digital customer’s journey, providing omnichannel digital touchpoints for the ease of use for the customers, the digital foundation where the business is conducted, and the people who assist the business in order to prevent any problems that can potentially harm the digital business during the session is active. The additional elements of digital business that are generally in digital business and are important to consider are using existing technology to cut prices, getting data and providing a better consumer experience, accepting the concept of digital transformation and the cultural changes required, and exploring new business models that put consumer experience at the center of digital business strategies.
Besides digital business elements, there are also digital business models. A digital business model serves as a blueprint that contains basic information about the products or services offered, the target demographic, and a unique company plan that can have advantages over competitors. The digital business concept concerns how a business makes its existence through basic business planning so that it has clear objectives to carry out its business efficiently, and with basic planning, a business can be distinguished from competitors in the market. Aagaard in Bradley et al. explained that there are three types of digital business models (18):
1. Cost value (i.e., price transparency, consumption-based pricing, reverse auctions, buyer aggregation, rebates, and rewards)
2. Experience value (i.e., customer choice, personalization, automation, lower latency, and any device at any time)
3. Platform value (i.e., marketplaces, crowdsourcing, peer-to-peer, sharing economy, and data monetization).
Meanwhile, according to Weill and Woerner, digital business concepts and designs are distinguished based on the correlation between the company’s knowledge of consumers such as consumer information and consumer goals or knowing completely, with business designs such as important company decisions (19). The concept can be seen in Figure 2.
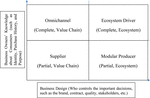
Figure 2. Business concept model. Source: Weill and Woerner (19).
Concepts based on these correlations can be divided into four types, namely, suppliers who are producers that sell goods or services through other businesses/shops; omnichannel, an integrated value chain that creates various products with various consumer channels to match daily needs; modular producer, a provider of features or services that connect products or services with systems as they are connected; and ecosystem driver, a coordinated network of businesses, electronic devices, and consumers to create value for all parties involved, for instance, setting the direction of the parts and ensuring good customer service, including complementary and sometimes competing products.
3.3. Opportunities in digital business
There are two ways for digital entrepreneurs to start their business, either selling through e-commerce or building their own digital company by creating their own products or services online. When compared, using an e-commerce site is easier to implement than creating your own website, but if they have plans to build a digital company to conduct transactions exclusively in their own digital environment, then creating a website is the superior choice.
E-commerce sites vary greatly. In Indonesia, there are more than 10 e-commerce sites that Indonesians use to conduct online transactions. Here are the five most used e-commerce sites by monthly visits in Indonesia as of Q3 2022 (20), as shown in Table 1.
In comparison, shown in Table 2 are the five most used e-commerce sites by monthly visits worldwide as of Q3 2022 (21).
These data mean that people have very strong purchasing power in making purchases through e-commerce, mostly from sites that have been established and provided as online sales places. This creates an opportunity for entrepreneurs as well as business owners to start their business by selling their products or services through the help of e-commerce sites. It is expected that these numbers will increase from time to time.
If an entrepreneur has a plan to build their own company digitally, then he will focus more on building a website. Building a website might cost a bit more than setting up a shop on e-commerce sites, but it makes selling products and services more personalized and exclusive. Connie explained that there are eight steps in building a website for a digital company (22):
1. Acquire a domain name that matches the company’s name.
2. Own an email address for conducting business.
3. Choose website builders, such as Wix, Squarespace, and Weebly dan Wordpress.
4. Pick a website template to make the website more colorful.
5. Add contents to the website, such as products or services provided, and the owner or customer service contact.
6. Integrate features such as live chat with customer service, social media, blog posts, and so on.
7. Utilize search engine optimization, as it is used to make it easier for people to find the company‘s website through search engines.
8. Publish the website, monitor the website, and update it when needed.
Another aspect that needs to be noticed when building a digital business is what industry should the business runs on. It should be noted that there are still some industries that have not been or are in the process of integration toward digitalization. Figure 3 shows the part of the industry that has been influenced, is being influenced, and has not and will be influenced.
Industries that have not yet or will digitize indicates that, within the industry, there is the creation and development of new technologies that adapt to current technological developments and to survive the changes require rapid adaptation. According to Jain (23), analysts predicted that 67% of global companies will digitize as their corporate strategy. This statement means that existing businesses will change the way they do business, and new businesses in the future will do the same to compete with other companies. Digital entrepreneurs can take this opportunity to create an industry that can change the way an industry operates, and compete to be better than existing competitors.
Digital business and online sales according to Cohen (in Jackson, Harris, and Eckersley), stated by Pleasants that, in 1999, it was estimated that sales from online business in the United States reached US$36.6 billion, US$3.5 billion in Europe, and US$2.8 in Asia Pacific. The transition of digital business will widen, emphasized by the fact that digital business has considerable potential to expand very aggressively, so understanding digital business in the market is very important.
3.4. Differences between traditional and digital business
Although, in the business sector, where all forms of business have been digitized, from transactions to interactions between buyers and sellers, there are several things that distinguish digital business from traditional business, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each form of business, traditional business is still the basic form of running a business, so there are advantages and disadvantages that can be shown from businesses that have been digitized and businesses that have not been digitized. Table 3 will first explain the differences between digital entrepreneurship and traditional entrepreneurship.
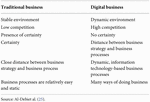
It has been established before that the rise of digital entrepreneurship has affected the flow and the way businesses conduct themselves. Traditional businesses still play a very important role in the society, especially in developing countries where building a business involves methods from the traditional knowledge of business building, but even then, they eventually integrate themselves into the digital world, connecting and reaching people outside of the local range. Table 4 explains the difference between traditional business and digital business.
Al-Debi, El-Haddadeh, and Avison argued that the reasoning behind the comparison above is due to the shift that the business world experienced from the traditional way of doing business to the new way of digital business, which is engulfed with a high level of complexity and rapid change (25). Thus, it is proven that, as time progresses, businesses will go digital eventually or at least be connected with digital applications.
3.5. How to start digital business as an entrepreneur
In today’s digital era, many entrepreneurs have built their businesses digitally, following the development of technology and the influence of globalization. Consumer behavior has changed, technology is getting more sophisticated, and the influence of globalization is increasingly unavoidable. Therefore, entrepreneurs must adapt in order to enter into the market share and survive as one of the digital business owners.
In general, to build a digital business, an entrepreneur must pay attention to several key factors that are important in his digital business (26):
1. Prepare capital and financial planning and business planning.
Analyze capabilities, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats through SWOT analysis.
1. Select the place and type of product to be offered.
2. Analyze the market and competitors.
3. Choose the desired platform for doing business, or build a website domain.
4. Create a prototype of the idea generated.
5. Promote the digital business that has been built.
Digital businesses that are assisted by platforms and digital businesses that use website domains have slightly different mechanisms, so they have several differences in running their business. Cohen in Jackson, Harris, and Eckersley (16) explained few ways that can help online businesses do well in the digital marketplace:
1. Check with local experts on cultural, legal, and technical matters so that the business does not create problems due to consumer misunderstandings arising from the digital business messages or notifications.
2. Try your best to provide a simple yet attractive interface, and have options for different languages so that users with limited foreign language skills can use their local language. In addition, do repeated tests to avoid technical errors and misunderstandings that arise from digital business design.
3. If the item being sold has a size, given the option to measure it through different calculations. Buyers from America may be confused by the measurements listed by European sellers because the items sold are measured in centimeters (cm), while the majority of Americans use measurements that are measured in inches (in).
4. Provide clear information on item information, logistics, and terms and conditions for each country and platform. Buyers may be disappointed if some information is not clearly provided to them, such as customs fees that the seller is not informed of.
5. Payment methods should be country-specific.
6. In the checkout system, the payment form should be applicable to all countries, as each country has different postal codes, phone numbers, and addresses that may not match a form that is only provided for one country.
7. Offer currency conversion to facilitate the amount of money needed to send money by the buyer.
Additionally, the understanding of culture in international businesses is also needed, such as esthetics, religion/belief, education, values and attitudes, social organization, technology and material culture, language, law, and politics (16). These cultures are important because every customer who visits a business from time to time will have a different background, different norms, and different beliefs that need to be understood and respected by every other person. Failing to do these tasks will harm the potential profit and opportunities of businesses.
4. Conclusion
Digital business is a transition from traditional business as a result of the effects of globalization. Digital business is a form of business that involves transactions between buyers and sellers without having to meet each other in person. Digital business makes it easy for sellers to offer goods and services to buyers and makes it easy for buyers to make transactions through online ordering and online payments. Although there are many advantages that digital business has, traditional business still has some aspects that digital business does not have, and digital business cannot be separated from the obstacles and weaknesses it has. Therefore, to implement a digital business, extensive knowledge and good planning are needed so that the digital business can be implemented.
Young entrepreneurs, through digital business, can become digital entrepreneurs. Digital entrepreneur can run their digital business with the platform provided without having to spend a lot of money. A young entrepreneur, in this digital era, must have extensive innovation and have traditional entrepreneurial values, even though it has transitioned through digital, because these values will be a guide for the entrepreneur to run the digital business. A young entrepreneur must take advantage of new and vast opportunities because of the effects of globalization, as through digital business and the effects of globalization, access to information, access to communication, and business development have opened up more widely, giving rise to many opportunities to release ideas and innovations into opportunities that can be utilized.
However, this transition stage is still ongoing and has not yet reached the end of the transition. Consumers are not yet fully engaged in digital businesses and services, as there are still some consumers who prefer to avoid the transition and stick to traditional values. The concept of digital business is still considered new because there are still many developments that can be done to make digital business perfect as a whole.
Author contributions
HH: introduction, research methodology, conclusion, and crosschecking references. KF: describing digital entrepreneurship. KH: elements and models of digital business for digital entrepreneurs. WJ: differences between traditional and digital business. LT: opportunities in digital business. LV: How to start a digital business as an entrepreneur. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank a university lecturer from University Widya Dharma Pontianak, Mr. Georgerius Graceallah, SE, and MM as an entrepreneurship class lecturer for teaching entrepreneurship and giving structured assignments in the form of a review paper, which then converted into this published paper for other researchers and public read.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Supriyanto AS, Maharani V. Metodologi Penelitian Manajemen Sumberdaya Manusia: Teori, Kuesioner, dan Analisis Data. Malang: UIN-Maliki Press (2013).
2. Chang W. Metodologi Penulisan Ilmiah: Teknik Penulisan Esai, Skripsi, Tesis, & Disertasi untuk Mahasiswa. Jakarta: Penerbut Erlangga (2014).
3. Merriam-Webster. Merriam-Webster’s Advanced Learner’s English Dictionary. 9th ed. Springfield: Merriam-Webster, Inc (2016).
4. Frederick H, O’Connor A, Kuratko DF. Entrepreneurship: Theory, Process, Practice. 4th ed. South Melbourne: Cengage Learning Australia (2016).
6. Dollinger MJ. Entrepreneurship: Strategies and Resources. 4th ed. Lombard: Marsh Publications (2008).
7. Mtima L. A copyright social utility and social justice interdependence: a paradigm for intellectual property empowerment and digital entrepreneurship. West Virgina Law Rev. (2009) 112:97–151.
8. Davidson E, Vaast E. Digital Entrepreneurship and its Sociomaterial Enactment. Proceedings of the 43rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. Koloa (2010).
9. Kelestyn B, Henfridsson O. Everyday Digital Entrepreneurship: The Inception, Shifts, and Scaling of Future Shaping Practices. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Information Systems. Auckland (2014).
10. Komarkova I, Gagliardi D, Conrads J, Collado A. Entrepreneurship Competence: An Overview of Existing Concepts, Policies and Initiatives. Seville: European Commission (2015).
11. Bogdanowicz M. Digital Entrepreneurship Barriers and Drivers: The Need for a Specific Measurement Framework. Seville: European Commission (2015).
12. Gujrati R, Uygun H. Digital Entrepreneurship. Southampton: Tradepreneur Global Academic Platform (2020).
13. Giones F, Brem A. Digital technology entrepreneurship: a definition and research agenda. Technology Innov Manage Rev. (2017) 7:44–51.
14. Bisht S, Prakash N, Saraswat S, Srivastava S. Digital entrepreneurship and the bottom of the pyramid-A conceptual framework. Int J Recent Trends Bus Tour. (2019) 3:33–42.
15. Wirtz BW. Digital Business Models: Concepts, Models, and the Alphabet Case Study. Cham: Springer (2019).
17. Afshar V. Accenture Digital: 7 Digital Business Transformation Lessons. New York City, NY: HuffPost (2015).
18. Aagaard A. Digital Business Models: Driving Transformation and Innovation. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan (2018).
19. Weill P, Woerner SL. What’s Your Digital Business Model? Six Questions to Help You Build the Next Generation Enterprise. Boston, MA: Harvard Business Review Press (2018).
21. Boukarroum A. Charts: Top Global Marketplaces by Number of Visits. Traverse City, MI: Practical Ecommerce (2023).
22. Connie W. How to Build a Business Website in 2023: 8 Simple Steps. Austin, TX: Website Building Expert (2023).
23. Jain V. Emerging Digital Business Opportunities and Value. Arlington, MA: Cutter Consorium (2017).
24. Baierl R, Behrens J, Brem A. Digital Entrepreneurship: Interfaces between Digital Technologies and Entrepreneurship. Cham: Springer (2019).
25. Al-Debi MM, El-Haddadeh R, Avison D. Defining the Business Model in the New World of Digital Business. Proceedings of the AMCIS 2008 Proceedings. Toronto (2008).